CBD stands for cannabidiol. Cannabidiol, is one of the primary natural cannabinoids found in the industrial hemp plant.
WHAT ARE CANNABINOIDS?
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that bind the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) receptors throughout your brain and body. There are over 113 known different cannabinoids found in hemp.
WHAT ARE CANNABINOID RECEPTORS?
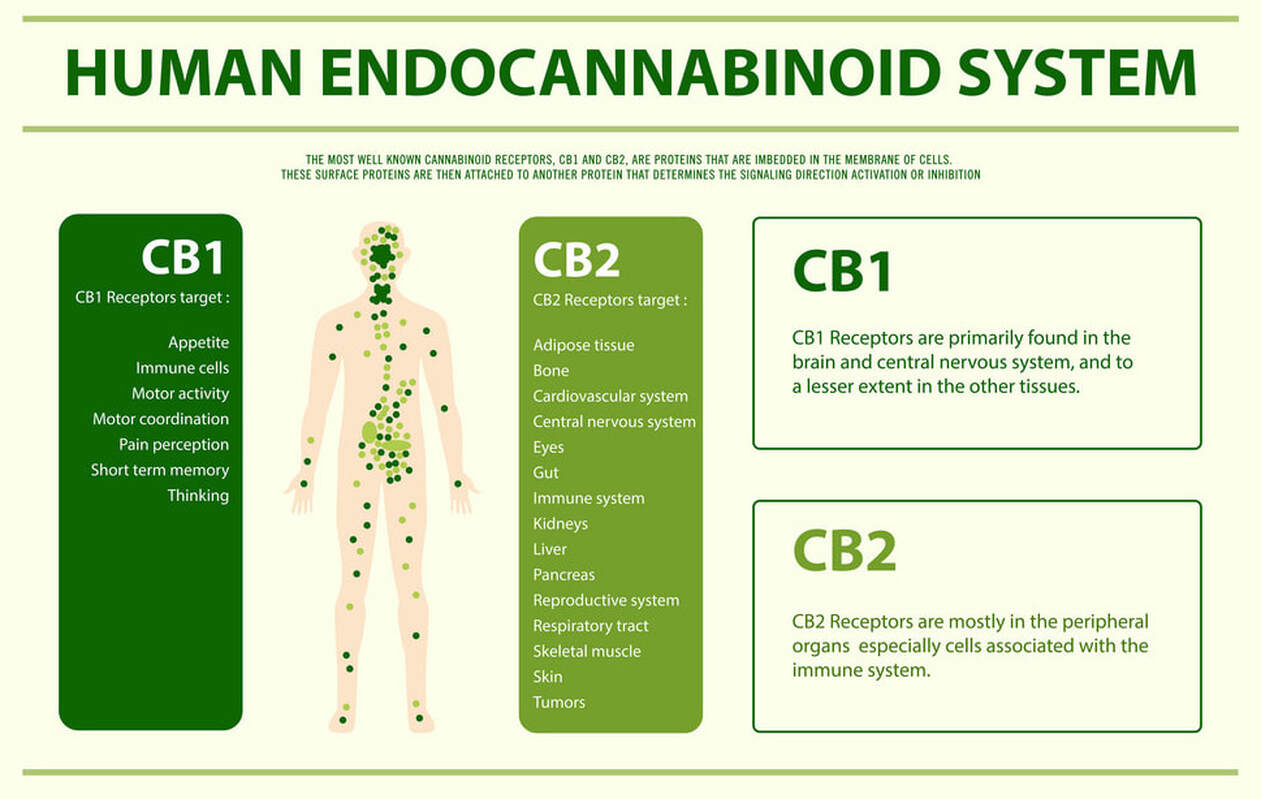
Cannabinoid receptors are embedded in cell membranes throughout your body. Researchers have identified two cannabinoid receptors: CB-1, predominantly present in the nervous system, connective tissues, gonads, glands, and organs. CB-2, predominantly found in the immune system and its associated structures.
CBD is one of over a 100 naturally occurring compounds found in the resinous flowers, leaves, stalk, and roots of cannabis, a plant with a rich history as a medicine going back thousands of years. Cannabis grows as either Marijuana or Hemp. Marijuana is rich in THC and is commonly associated with getting “high”. Marijuana does contain CBD, however often in low levels.
Hemp is related to Marijuana. It looks and smells similar, however Hemp contains very low levels of THC. The male plants produce a large mass of seeds that are used to produce Hempseed oil and the stalks are used for their extremely strong fibers.
The female Hemp plants grow with often high concentrations of CBD and thus are mainly used for the extraction and production of CBD products. Today the therapeutic properties of CBD are being tested and confirmed by scientists and doctors around the world. A safe, non-addictive substance, CBD is one of more than a hundred “phytocannabinoids,” which are unique to cannabis and endow the plant with its robust therapeutic profile.
Legal CBD products contain less than .3% THC. Nearly no trace. Both CBD and THC have significant therapeutic attributes. But unlike THC, CBD does not make a person feel “stoned” or intoxicated. That’s because CBD and THC act in different ways on different receptors in the brain and body.
CBD can actually lessen or neutralize the psychoactive effects of THC, depending on how much of each compound is consumed. Many people want the health benefits of cannabis without the high – or with less of a high.
The fact that CBD is therapeutically potent as well as non-intoxicating, and easy to use as a CBD oil, makes it an appealing treatment option for those who are cautious about trying cannabis for the first time.
Many people are seeking alternatives to pharmaceuticals with harsh side effects – medicine more in synch with natural processes. By tapping into how we function biologically on a deep level, CBD may provide relief for a wide range of conditions through natural plant remedies.
CBD is one of over a 100 naturally occurring compounds found in the resinous flowers, leaves, stalk, and roots of cannabis, a plant with a rich history as a medicine going back thousands of years. Cannabis grows as either Marijuana or Hemp. Marijuana is rich in THC and is commonly associated with getting “high”. Marijuana does contain CBD, however often in low levels.
Hemp is related to Marijuana. It looks and smells similar, however Hemp contains very low levels of THC. The male plants produce a large mass of seeds that are used to produce Hempseed oil and the stalks are used for their extremely strong fibers.
The female Hemp plants grow with often high concentrations of CBD and thus are mainly used for the extraction and production of CBD products. Today the therapeutic properties of CBD are being tested and confirmed by scientists and doctors around the world. A safe, non-addictive substance, CBD is one of more than a hundred “phytocannabinoids,” which are unique to cannabis and endow the plant with its robust therapeutic profile.
Legal CBD products contain less than .3% THC. Nearly no trace. Both CBD and THC have significant therapeutic attributes. But unlike THC, CBD does not make a person feel “stoned” or intoxicated. That’s because CBD and THC act in different ways on different receptors in the brain and body.
CBD can actually lessen or neutralize the psychoactive effects of THC, depending on how much of each compound is consumed. Many people want the health benefits of cannabis without the high – or with less of a high.
The fact that CBD is therapeutically potent as well as non-intoxicating, and easy to use as a CBD oil, makes it an appealing treatment option for those who are cautious about trying cannabis for the first time.
Many people are seeking alternatives to pharmaceuticals with harsh side effects – medicine more in synch with natural processes. By tapping into how we function biologically on a deep level, CBD may provide relief for a wide range of conditions through natural plant remedies.
HOW DOES CBD WORK?
CBD interacts with our bodies in a variety of ways. One of the main ways it impacts us is by mimicking and augmenting the effects of the compounds in our bodies called “endogenous cannabinoids” - so named because of their similarity to the compounds found in the cannabis plant. These “endocannabinoids” are part of a regulatory system, mentioned earlier, called the “endocannabinoid system” that all vertebrates on this planet have within us.
The discovery of the endocannabinoid system has significantly advanced our understanding of health and disease. It has major implications for nearly every area of medical science and helps to explain how and why CBD is such a versatile compound.
The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating a broad range of physiological processes that affect our everyday experience – our mood, our energy level, our intestinal fortitude, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, how we experience pain, stress, hunger, and more.
What happens if the endocannabinoid system doesn’t function properly? What are the consequences of a chronically deficient or overactive endocannabinoid system?
In a word, DISEASE (Dis-Ease)
Cutting-edge science has shown that the endocannabinoid system is dysregulated in nearly all pathological conditions. Thus, it stands to reason that “modulating/supplementing endocannabinoid system activity may have therapeutic potential in almost all diseases affecting humans,” as Pal Pacher and George Kunos, scientists with the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), suggested in a 2014 publication.
By supplementing/supporting an active and healthy endocannabinoid system and enhancing endocannabinoid tone, one should experience a much healthier overall functioning system.
The discovery of the endocannabinoid system has significantly advanced our understanding of health and disease. It has major implications for nearly every area of medical science and helps to explain how and why CBD is such a versatile compound.
The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating a broad range of physiological processes that affect our everyday experience – our mood, our energy level, our intestinal fortitude, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, how we experience pain, stress, hunger, and more.
What happens if the endocannabinoid system doesn’t function properly? What are the consequences of a chronically deficient or overactive endocannabinoid system?
In a word, DISEASE (Dis-Ease)
Cutting-edge science has shown that the endocannabinoid system is dysregulated in nearly all pathological conditions. Thus, it stands to reason that “modulating/supplementing endocannabinoid system activity may have therapeutic potential in almost all diseases affecting humans,” as Pal Pacher and George Kunos, scientists with the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), suggested in a 2014 publication.
By supplementing/supporting an active and healthy endocannabinoid system and enhancing endocannabinoid tone, one should experience a much healthier overall functioning system.
So Much More to be Discovered
Research has really just began to the health benefits of CBD and the entourage effect of Full Spectrum Cannabinoid extracts and products. We will see this medicine greatly improve the health of those who form a relationship with it.